Roksindol
| |||
| (IUPAC) ime | |||
|---|---|---|---|
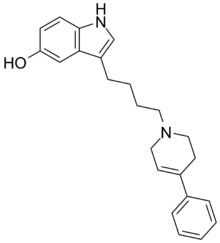
| 3-[4-(4-fenil-3,6-dihidro-2H-piridin-1-il)butil]-1H-indol-5-ol | |||
| Klinički podaci | |||
| Identifikatori | |||
| CAS broj | 112192-04-8 | ||
| ATC kod | nije dodeljen | ||
| PubChem[1][2] | 219050 | ||
| ChemSpider[3] | 189880 | ||
| UNII | 43227SMS0O | ||
| Hemijski podaci | |||
| Formula | C23H26N2O | ||
| Mol. masa | 346,47 g/mol | ||
| SMILES | eMolekuli & PubHem | ||
| |||
| Farmakoinformacioni podaci | |||
| Trudnoća | ? | ||
| Pravni status | |||
Roksindol (EMD-49,980) je dopaminergični i serotonergični lek koji je originalno bio razvijen za lečenje šizofrenije.[4][5][6] U kliničkim ispitivanjima njegova antipsihotička efikasnost je bila skromna, ali je neočekivano nađeno da proizvodi potentne i brze antidepresantne i anksiolitičke efekte.[5][6] Konsekventno, roksindol je dalje istražen za primenu u lečenju depresije.[4][7][7] On je takođe istražen kao terapija za Parkinsonovu bolest i lečenje prolaktinoma.[8][9]
Roksindol deluje kao agonist na sledećim receptorima:[10][11]
- D2 receptor (pKi = 8.55)
- D3 receptor (pKi = 8.93)
- D4 receptor (pKi = 8.23)
- 5-HT1A receptor (pKi = 9.42)
Reference[uredi | uredi kod]
- ↑ Li Q, Cheng T, Wang Y, Bryant SH (2010). „PubChem as a public resource for drug discovery.”. Drug Discov Today 15 (23-24): 1052-7. DOI:10.1016/j.drudis.2010.10.003. PMID 20970519. edit
- ↑ Evan E. Bolton, Yanli Wang, Paul A. Thiessen, Stephen H. Bryant (2008). „Chapter 12 PubChem: Integrated Platform of Small Molecules and Biological Activities”. Annual Reports in Computational Chemistry 4: 217-241. DOI:10.1016/S1574-1400(08)00012-1.
- ↑ Hettne KM, Williams AJ, van Mulligen EM, Kleinjans J, Tkachenko V, Kors JA. (2010). „Automatic vs. manual curation of a multi-source chemical dictionary: the impact on text mining”. J Cheminform 2 (1): 3. DOI:10.1186/1758-2946-2-3. PMID 20331846. edit
- ↑ 4,0 4,1 Gründer G, Wetzel H, Hammes E, Benkert O (1993). „Roxindole, a dopamine autoreceptor agonist, in the treatment of major depression”. Psychopharmacology 111 (1): 123–6. DOI:10.1007/BF02257418. PMID 7870927.
- ↑ 5,0 5,1 Klimke A, Klieser E (July 1991). „Antipsychotic efficacy of the dopaminergic autoreceptor agonist EMD 49980 (Roxindol). Results of an open clinical study”. Pharmacopsychiatry 24 (4): 107–12. DOI:10.1055/s-2007-1014451. PMID 1684439.
- ↑ 6,0 6,1 Kasper S, Fuger J, Zinner HJ, Bäuml J, Möller HJ (March 1992). „Early clinical results with the neuroleptic roxindole (EMD 49,980) in the treatment of schizophrenia--an open study”. European Neuropsychopharmacology : the Journal of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology 2 (1): 91–5. DOI:10.1016/0924-977X(92)90041-6. PMID 1353388.
- ↑ 7,0 7,1 Maj J, Kolodziejczyk K, Rogóz Z, Skuza G (1996). „Roxindole, a potential antidepressant. I. Effect on the dopamine system”. Journal of Neural Transmission (Vienna, Austria : 1996) 103 (5): 627–41. PMID 8811507.
- ↑ Bravi D, Davis TL, Mouradian MM, Chase TN (April 1993). „Treatment of Parkinson's disease with the partial dopamine agonist EMD 49980”. Movement Disorders : Official Journal of the Movement Disorder Society 8 (2): 195–7. DOI:10.1002/mds.870080214. PMID 8097280.
- ↑ Jaspers C, Benker G, Reinwein D (June 1994). „Treatment of prolactinoma patients with the new non-ergot dopamine agonist roxindol: first results”. The Clinical Investigator 72 (6): 451–6. PMID 7950157.
- ↑ Newman-Tancredi A, Cussac D, Audinot V, Millan MJ (June 1999). „Actions of roxindole at recombinant human dopamine D2, D3 and D4 and serotonin 5-HT1A, 5-HT1B and 5-HT1D receptors”. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology 359 (6): 447–53. PMID 10431754.
- ↑ Heinrich T, Böttcher H, Bartoszyk GD, Greiner HE, Seyfried CA, Van Amsterdam C (September 2004). „Indolebutylamines as selective 5-HT(1A) agonists”. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 47 (19): 4677–83. DOI:10.1021/jm040792y. PMID 15341483.
Spoljašnje veze[uredi | uredi kod]
Antipsihotici (neuroleptici) (N05A) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Tipični | Benzamidi: Levosulpirid • Nemonaprid • Sulpirid • Sultoprid • Tiaprid • Veraliprid
Butirofenoni: Azaperon • Benperidol • Bromperidol • Droperidol • Fluanizon • Haloperidol # • Lenperon • Moperon • Pipamperon • Spiperon • Timiperon • Trifluperidol Difenilbutilpiperidini: Klopimozid • Fluspirilen • Penfluridol • Pimozid Fenotiazini: Acepromazin • Acetofenazin • Butaperazin • Karfenazin • Hloracizin • Hlorproetazin • Hlorpromazin • Cijamemazin • Diksirazin • Fluacizin • Flufenazin • Levomepromazin/Metotrimeprazin • Mezoridazin • Perazin • Pericijazin • Perfenazin • Piperacetazin • Pipotiazin • Prohlorperazin • Promazin • Prometazin • Propiomazin • Sulforidazin • Tietilperazin • Tiopropazat • Tioproperazin • Tioridazin • Trifluoperazin • Triflupromazin Tioksanten: Hlorprotiksen • Klopentiksol • Flupentiksol • Tiotiksen • Zuklopentiksol Triciklici: Butaklamol • Fluotracen • Loksapin • Trimipramin Drugi: Protipendil | ||
| Atipični | Benzamidi: Amisulprid • Remoksiprid‡
Butirofenoni: Cinuperon • Melperon • Setoperon Benzo(izo)oksazolpiperidini: Iloperidon • Okaperidon • Paliperidon • Risperidon # Benzo(izo)tiazolpiperazini: Lurasidone • Perospiron • Revospiron • Tiospiron • Ziprasidon Difenilbutilpiperazini: Amperozid Fenilpiperazini: Aripiprazol • Bifeprunoks • Brekspiprazol† • Elopiprazol • Umespiron Triciklici: Amoksapin • Asenapin • Karpipramin • Klocapramin • Klorotepin • Klotiapin • Klozapin # • Fluperlapin • Gevotrolin • Metitepin • Mosapramin • NDMC • Olanzapin • Pihindon • Kvetijapin • Tenilapin • Zotepin Drugi: Blonanserin • Kariprazin • Molindon • Pimavanserin • Roksindol • Sarizotan • Sertindol • Spiramid • Zikronapin† | ||
| Drugi | Alstonin • Azaciklonol • Kanabidiol • Mazapertin§ • Mifepriston • Oksipertin • Reserpin • Rimkazol • Sekretin • Talnetant§ • Tetrabenazin • Vabicaserin | ||
#WHO-EM • ‡Povučeni sa tržišta • Klinička ispitivanja: †Faza III • §Nije dospeo do faze III | |||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||