Flesinoksan
Prijeđi na navigaciju
Prijeđi na pretragu
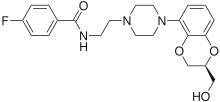
| |||
| (IUPAC) ime | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 4-fluoro-N-(24-[(2S)-2-(hidroksimetil)-2,3-dihidro-1,4-benzodioksin-5-il]piperazin-1-il}etil)benzamid | |||
| Klinički podaci | |||
| Identifikatori | |||
| CAS broj | 98206-10-1 | ||
| ATC kod | nije dodeljen | ||
| PubChem[1][2] | 57347 | ||
| ChemSpider[3] | 51700 | ||
| UNII | 3V574S89E1 | ||
| KEGG[4] | D02568 | ||
| Hemijski podaci | |||
| Formula | C22H26FN3O4 | ||
| Mol. masa | 415,458 g/mol | ||
| SMILES | eMolekuli & PubHem | ||
| |||
| Farmakoinformacioni podaci | |||
| Trudnoća | ? | ||
| Pravni status | Nije kontrolisana supstanca | ||
| Način primene | Oralno | ||
Flesinoksan (DU-29,373) je potentan i selektivan parcijalni/skoro-pun agonist 5-HT1A receptora iz fenilpiperazinske klase.[5][6][7]
Flesinoksan je originalno razvijen kao antihipertenziv,[5][6][8] a kasnije je utvrđeno da poseduje antidepresivne i anksiolitske efekte na životinjama.[9][10] Konsekventno, on je klinička ispitivanja su sprovedana za tretman kliničke depresije i generalizovanog anksioznog poremećaja. Utvrđeno je da je ima robastnu efikasnost sa veoma visokom tolerabilnošću,[11][12] ali je zbog nepoznatih razloga njegov razvoj prekinut. Kod pacijenata on poboljšava REM san, snižava telesnu temperaturu, i povišava nivoe ACTH-a, kortizola, prolaktina, i hormona rasta.[12][13]
Reference[uredi | uredi kod]
- ↑ Li Q, Cheng T, Wang Y, Bryant SH (2010). „PubChem as a public resource for drug discovery.”. Drug Discov Today 15 (23-24): 1052-7. DOI:10.1016/j.drudis.2010.10.003. PMID 20970519.
- ↑ Evan E. Bolton, Yanli Wang, Paul A. Thiessen, Stephen H. Bryant (2008). „Chapter 12 PubChem: Integrated Platform of Small Molecules and Biological Activities”. Annual Reports in Computational Chemistry 4: 217-241. DOI:10.1016/S1574-1400(08)00012-1.
- ↑ Hettne KM, Williams AJ, van Mulligen EM, Kleinjans J, Tkachenko V, Kors JA. (2010). „Automatic vs. manual curation of a multi-source chemical dictionary: the impact on text mining”. J Cheminform 2 (1): 3. DOI:10.1186/1758-2946-2-3. PMID 20331846.
- ↑ Joanne Wixon, Douglas Kell (2000). „Website Review: The Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes — KEGG”. Yeast 17 (1): 48–55. DOI:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0061(200004)17:1<48::AID-YEA2>3.0.CO;2-H.
- ↑ 5,0 5,1 Schoeffter P, Hoyer D. (1988). „Centrally acting hypotensive agents with affinity for 5-HT1A binding sites inhibit forskolin-stimulated adenylate cyclase activity in calf hippocampus.”. Br J Pharmacol. 95 (3): 975–985. PMC 1854240. PMID 3207999.
- ↑ 6,0 6,1 Pitchot W, Wauthy J, Legros JJ, Ansseau M (March 2004). „Hormonal and temperature responses to flesinoxan in normal volunteers: an antagonist study”. European Neuropsychopharmacology 14 (2): 151–5. DOI:10.1016/S0924-977X(03)00108-1. PMID 15013031.
- ↑ Hadrava V, Blier P, Dennis T, Ortemann C, de Montigny C (October 1995). „Characterization of 5-hydroxytryptamine1A properties of flesinoxan: in vivo electrophysiology and hypothermia study”. Neuropharmacology 34 (10): 1311–26. DOI:10.1016/0028-3908(95)00098-Q. PMID 8570029.
- ↑ Wouters W, Tulp MT, Bevan P (May 1988). „Flesinoxan lowers blood pressure and heart rate in cats via 5-HT1A receptors”. European Journal of Pharmacology 149 (3): 213–23. DOI:10.1016/0014-2999(88)90651-6. PMID 2842163.
- ↑ van Hest A, van Drimmelen M, Olivier B (1992). „Flesinoxan shows antidepressant activity in a DRL 72-s screen”. Psychopharmacology 107 (4): 474–9. DOI:10.1007/BF02245258. PMID 1351303.
- ↑ Rodgers RJ, Cole JC, Davies A (August 1994). „Antianxiety and behavioral suppressant actions of the novel 5-HT1A receptor agonist, flesinoxan”. Pharmacology, Biochemistry, and Behavior 48 (4): 959–63. DOI:10.1016/0091-3057(94)90205-4. PMID 7972301.
- ↑ Grof P, Joffe R, Kennedy S, Persad E, Syrotiuk J, Bradford D (1993). „An open study of oral flesinoxan, a 5-HT1A receptor agonist, in treatment-resistant depression”. International Clinical Psychopharmacology 8 (3): 167–72. DOI:10.1097/00004850-199300830-00005. PMID 8263314.
- ↑ 12,0 12,1 Marc Ansseau, William Pitchot, Antonio Gonzalez Moreno, Jacques Wauthy, Patrick Papart (2004). „Pilot study of flesinoxan, a 5-HT1A agonist, in major depression: Effects on sleep REM latency and body temperature.”. Human Psychopharmacology: Clinical and Experimental 8 (4): 279–283. DOI:10.1002/hup.470080407. Arhivirano iz originala na datum 2012-12-17. Pristupljeno 2014-04-05.
- ↑ Pitchot W, Wauthy J, Legros JJ, Ansseau M (March 2004). „Hormonal and temperature responses to flesinoxan in normal volunteers: an antagonist study”. European Neuropsychopharmacology : the Journal of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology 14 (2): 151–5. DOI:10.1016/S0924-977X(03)00108-1. PMID 15013031.