Histaminski H3 receptor
| edit |
| Histaminski receptor H3 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifikatori | |||||||||||
| Simboli | HRH3; GPCR97; HH3R | ||||||||||
| Vanjski ID | OMIM: 604525 MGI: 2139279 HomoloGene: 5232 IUPHAR: H3 GeneCards: HRH3 Gene | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Pregled RNK izražavanja | |||||||||||
 | |||||||||||
 | |||||||||||
| podaci | |||||||||||
| Ortolozi | |||||||||||
| Vrsta | Čovek | Miš | |||||||||
| Entrez | 11255 | 99296 | |||||||||
| Ensembl | ENSG00000101180 | ENSMUSG00000039059 | |||||||||
| UniProt | Q9Y5N1 | P58406 | |||||||||
| RefSeq (mRNA) | NM_007232.2 | NM_133849.2 | |||||||||
| RefSeq (protein) | NP_009163.2 | NP_598610.1 | |||||||||
| Lokacija (UCSC) | Chr 20: 60.79 - 60.8 Mb | Chr 2: 179.83 - 179.84 Mb | |||||||||
| PubMed pretraga | [1] | [2] | |||||||||
Histaminski H3 receptori su izraženi u centralnom nervnom sistemu i u manjoj meri u perifernom nervnom sistemu, gde oni deluju kao autoreceptori u presinaptičkim histaminergičkim neuronima, i takođe kontrolišu promet histamina putem povratne inhibicije sinteze i oslobađanja.[1] H3 receptor takođe presinaptički inhibira otpuštanje brojnih drugih neurotransmitera (i.e. on deluje kao inhibitorni heteroreceptor) uključujući, ali verovatno ne samo dopamina, GABA, acetilholina, noradrenalina, i serotonina.
Genska sekvenca H3 receptora je samo oko 22% i 20% homologna sa H1 i H2 receptorima respektivno.
Tkivna distribucija[uredi | uredi kod]
Funkcija[uredi | uredi kod]
Poput svih histaminskih receptora H3 receptor je G protein spregnuti receptor. H3 receptor je spregnut sa Gi G proteinom, tako da dovodi do inhibicije formiranja cAMP. Takođe, β i γ podjedinice interaguju sa N-tipom naponom kontrolisanog kalcijumskog kanala, da redukuju dejstvo potencijalom posredovanog uliva kalcijuma i tako redukuju otpuštanje neurotransmitera.
H3 receptori funkcionišu kao presinaptički autoreceptori na histaminskim neuronima.[2]
Raznovrsnost izražavanja H3 receptora širom korteksa i podkorteksa je indikacija njegove sposobnosti da moduliše otpuštanje velikog broja neurotransmitera.
H3 receptori učestvuju u kontroli sitosti.[3]
Isoforme[uredi | uredi kod]
Postoji najmanje šest izoformi H3 receptora kod ljudi, i više od 20 je otkriveno do sada računajući druge vrste.[4] Kod pacova je do sad otkriveno šest podtipova H3 receptora, dok su kod miševa poznate tri.[5] Ti podtipovi imaju suptilne razlike u pogledu farmakologije (kao i distribucije, sudeći po istraživanjina na pacovima), ali njihove precizne fiziološke uloge nisu razjašnjene.
Farmakologija[uredi | uredi kod]
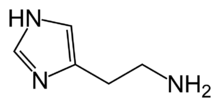
Terapeutski potencijal[uredi | uredi kod]
Ovaj receptor je predložen za biološki cilj u tretiranju poremećaja sna.[9] Takođe se smatra da modulacija dejstva ovog receptora može da nađe primenu u tretmanu neuropatičkog bola.[10]
Usled njegove sposobnosti modulacije drugih neurotransmitera, ligandi H3 receptora se istražuju za lečenje brojnih neuroloških poremećaja, uključujući gojaznost (zbog interakcije histaminskog i oreksinskog sistema), poremećaja kretanja (zbog modulacije dopamina i GABA putem H3 receptora u bazalnim ganglijama), šizofrenije i ADHD.[11]
Istorija[uredi | uredi kod]
- 1983 - H3 receptor je farmakološki identikovan.[12]
- 1988 - Utvrđeno je da H3 receptor posreduje inhibiciju otpuštanja serotonina moždanoj kori pacova.[13]
- 1997 - Pokazano je da H3 receptori modulišu ishemično otpuštanje norepinefrina kod životinja.[14]
- 1999 - H3 receptor je kloniran[15]
- 2000 - H3 receptori se nazivaju "novim kursom ishemije miokarda"[16]
- 2002 - H3(-/-) miš (miš bez ovog receptora)[17]
Reference[uredi | uredi kod]
- ↑ West RE, Zweig A, Shih NY, Siegel MI, Egan RW, Clark MA (1990). „Identification of two H3-histamine receptor subtypes” (abstract). Mol. Pharmacol. 38 (5): 610–3. PMID 2172771. Arhivirano iz originala na datum 2008-11-21. Pristupljeno 2014-05-03.
- ↑ „InterPro: IPR003980 Histamine H3 receptor”. InterPro. European Bioinformatics Institute.
- ↑ Attoub S, Moizo L, Sobhani I, Laigneau JP, Lewin MJ, Bado A (June 2001). „The H3 receptor is involved in cholecystokinin inhibition of food intake in rats”. Life Sci. 69 (4): 469–78. DOI:10.1016/S0024-3205(01)01138-9. PMID 11459437.
- ↑ Bakker RA (2004). „Histamine H3-receptor isoforms”. Inflamm. Res. 53 (10): 509–16. DOI:10.1007/s00011-004-1286-9. PMID 15597144.
- ↑ Rouleau A, Héron A, Cochois V, Pillot C, Schwartz JC, Arrang JM (2004). „Cloning and expression of the mouse histamine H3 receptor: evidence for multiple isoforms”. J. Neurochem. 90 (6): 1331–8. DOI:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2004.02606.x. PMID 15341517.
- ↑ Krueger KM, Witte DG, Ireland-Denny L, Miller TR, Baranowski JL, Buckner S, Milicic I, Esbenshade TA, Hancock AA. G protein-dependent pharmacology of histamine H3 receptor ligands: evidence for heterogeneous active state receptor conformations. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 2005 Jul;314(1):271-81. PMID 15821027
- ↑ Tedford CE, Phillips JG, Gregory R, Pawlowski GP, Fadnis L, Khan MA, Ali SM, Handley MK, Yates SL (1999). „Development of trans-2-(1H-imidazol-4-yl) cyclopropane derivatives as new high-affinity histamine H3 receptor ligands” (abstract). J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 289 (2): 1160–8. PMID 10215700. Arhivirano iz originala na datum 2009-01-07. Pristupljeno 2014-05-03.
- ↑ Esbenshade TA, Fox GB, Krueger KM, Baranowski JL, Miller TR, Kang CH, Denny LI, Witte DG, Yao BB, Pan JB, Faghih R, Bennani YL, Williams M, Hancock AA. Pharmacological and behavioral properties of A-349821, a selective and potent human histamine H3 receptor antagonist. Biochemical Pharmacology. 2004 September 1;68(5):933-45. PMID 15294456
- ↑ Passani MB, Lin JS, Hancock A, Crochet S, Blandina P (2004). „The histamine H3 receptor as a novel therapeutic target for cognitive and sleep disorders”. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 25 (12): 618–25. DOI:10.1016/j.tips.2004.10.003. PMID 15530639.
- ↑ Medhurst SJ, Collins SD, Billinton A, Bingham S, Dalziel RG, Brass A, Roberts JC, Medhurst AD, Chessell IP (2008). „Novel histamine H3 receptor antagonists GSK189254 and GSK334429 are efficacious in surgically-induced and virally-induced rat models of neuropathic pain.”. Pain 138 (1): 61–78. DOI:10.1016/j.pain.2007.11.006. PMID 18164820.
- ↑ Leurs R, Bakker RA, Timmerman H, de Esch IJ (2005). „The histamine H3 receptor: from gene cloning to H3 receptor drugs”. Nature reviews. Drug discovery 4 (2): 107–20. DOI:10.1038/nrd1631. PMID 15665857.
- ↑ Arrang JM, Garbarg M, Schwartz JC (1983). „Auto-inhibition of brain histamine release mediated by a novel class (H3) of histamine receptor”. Nature 302 (5911): 832–7. DOI:10.1038/302832a0. PMID 6188956.
- ↑ Schlicker E, Betz R, Göthert M (1988). „Histamine H3 receptor-mediated inhibition of serotonin release in the rat brain cortex”. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 337 (5): 588–90. DOI:10.1007/BF00182737. PMID 3412497.
- ↑ Hatta E, Yasuda K, Levi R (1997). „Activation of histamine H3 receptors inhibits carrier-mediated norepinephrine release in a human model of protracted myocardial ischemia” (abstract). J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 283 (2): 494–500. PMID 9353362. Arhivirano iz originala na datum 2008-06-30. Pristupljeno 2014-05-03.
- ↑ Lovenberg TW, Roland BL, Wilson SJ, Jiang X, Pyati J, Huvar A, Jackson MR, Erlander MG (1999). „Cloning and functional expression of the human histamine H3 receptor” (abstract). Mol. Pharmacol. 55 (6): 1101–7. PMID 10347254. Arhivirano iz originala na datum 2008-09-06. Pristupljeno 2014-05-03.
- ↑ Levi R, Smith NC (2000). „Histamine H3-receptors: a new frontier in myocardial ischemia” (abstract). J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 292 (3): 825–30. PMID 10688593. Arhivirano iz originala na datum 2008-12-02. Pristupljeno 2014-05-03.
- ↑ Toyota H, Dugovic C, Koehl M, Laposky AD, Weber C, Ngo K, Wu Y, Lee DH, Yanai K, Sakurai E, Watanabe T, Liu C, Chen J, Barbier AJ, Turek FW, Fung-Leung WP, Lovenberg TW (2002). „Behavioral characterization of mice lacking histamine H3 receptors”. Mol. Pharmacol. 62 (2): 389–97. DOI:10.1124/mol.62.2.389. PMID 12130692.
Literatura[uredi | uredi kod]
- Hill SJ, Ganellin CR, Timmerman H, et al. (1997). „International Union of Pharmacology. XIII. Classification of histamine receptors”. Pharmacol. Rev. 49 (3): 253–78. PMID 9311023.
- Malinowska B, Godlewski G, Schlicker E (1998). „Histamine H3 receptors--general characterization and their function in the cardiovascular system”. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 49 (2): 191–211. PMID 9670104.
- Leurs R, Hoffmann M, Wieland K, Timmerman H (2000). „H3 receptor gene is cloned at last”. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 21 (1): 11–2. DOI:10.1016/S0165-6147(99)01411-X. PMID 10637648.
- Leurs R, Bakker RA, Timmerman H, de Esch IJ (2005). „The histamine H3 receptor: from gene cloning to H3 receptor drugs”. Nature reviews. Drug discovery 4 (2): 107–20. DOI:10.1038/nrd1631. PMID 15665857.
- Esbenshade TA, Fox GB, Cowart MD (2006). „Histamine H3 receptor antagonists: preclinical promise for treating obesity and cognitive disorders”. Mol. Interv. 6 (2): 77–88, 59. DOI:10.1124/mi.6.2.5. PMID 16565470.
- Lovenberg TW, Roland BL, Wilson SJ, et al. (1999). „Cloning and functional expression of the human histamine H3 receptor”. Mol. Pharmacol. 55 (6): 1101–7. PMID 10347254.
- Nakamura T, Itadani H, Hidaka Y, et al. (2001). „Molecular cloning and characterization of a new human histamine receptor, HH4R”. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 279 (2): 615–20. DOI:10.1006/bbrc.2000.4008. PMID 11118334.
- Cogé F, Guénin SP, Audinot V, et al. (2001). „Genomic organization and characterization of splice variants of the human histamine H3 receptor”. Biochem. J. 355 (Pt 2): 279–88. DOI:10.1042/0264-6021:3550279. PMC 1221737. PMID 11284713.
- Silver RB, Poonwasi KS, Seyedi N, et al. (2002). „Decreased intracellular calcium mediates the histamine H3-receptor-induced attenuation of norepinephrine exocytosis from cardiac sympathetic nerve endings”. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (1): 501–6. DOI:10.1073/pnas.012506099. PMC 117589. PMID 11752397.
- Deloukas P, Matthews LH, Ashurst J, et al. (2002). „The DNA sequence and comparative analysis of human chromosome 20”. Nature 414 (6866): 865–71. DOI:10.1038/414865a. PMID 11780052.
- Wiedemann P, Bönisch H, Oerters F, Brüss M (2002). „Structure of the human histamine H3 receptor gene (HRH3) and identification of naturally occurring variations”. Journal of neural transmission (Vienna, Austria : 1996) 109 (4): 443–53. DOI:10.1007/s007020200036. PMID 11956964.
- Wellendorph P, Goodman MW, Burstein ES, et al. (2002). „Molecular cloning and pharmacology of functionally distinct isoforms of the human histamine H(3) receptor”. Neuropharmacology 42 (7): 929–40. DOI:10.1016/S0028-3908(02)00041-2. PMID 12069903.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). „Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences”. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. DOI:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Lozeva V, Tuomisto L, Tarhanen J, Butterworth RF (2004). „Increased concentrations of histamine and its metabolite, tele-methylhistamine and down-regulation of histamine H3 receptor sites in autopsied brain tissue from cirrhotic patients who died in hepatic coma”. J. Hepatol. 39 (4): 522–7. DOI:10.1016/S0168-8278(03)00353-2. PMID 12971961.
- Lippert U, Artuc M, Grützkau A, et al. (2004). „Human skin mast cells express H2 and H4, but not H3 receptors”. J. Invest. Dermatol. 123 (1): 116–23. DOI:10.1111/j.0022-202X.2004.22721.x. PMID 15191551.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). „The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)”. Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. DOI:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
Spoljašnje veze[uredi | uredi kod]
- „Histamine Receptors: H3”. IUPHAR Database of Receptors and Ion Channels. International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. Arhivirano iz originala na datum 2013-12-25.
- MeSH H3+receptors